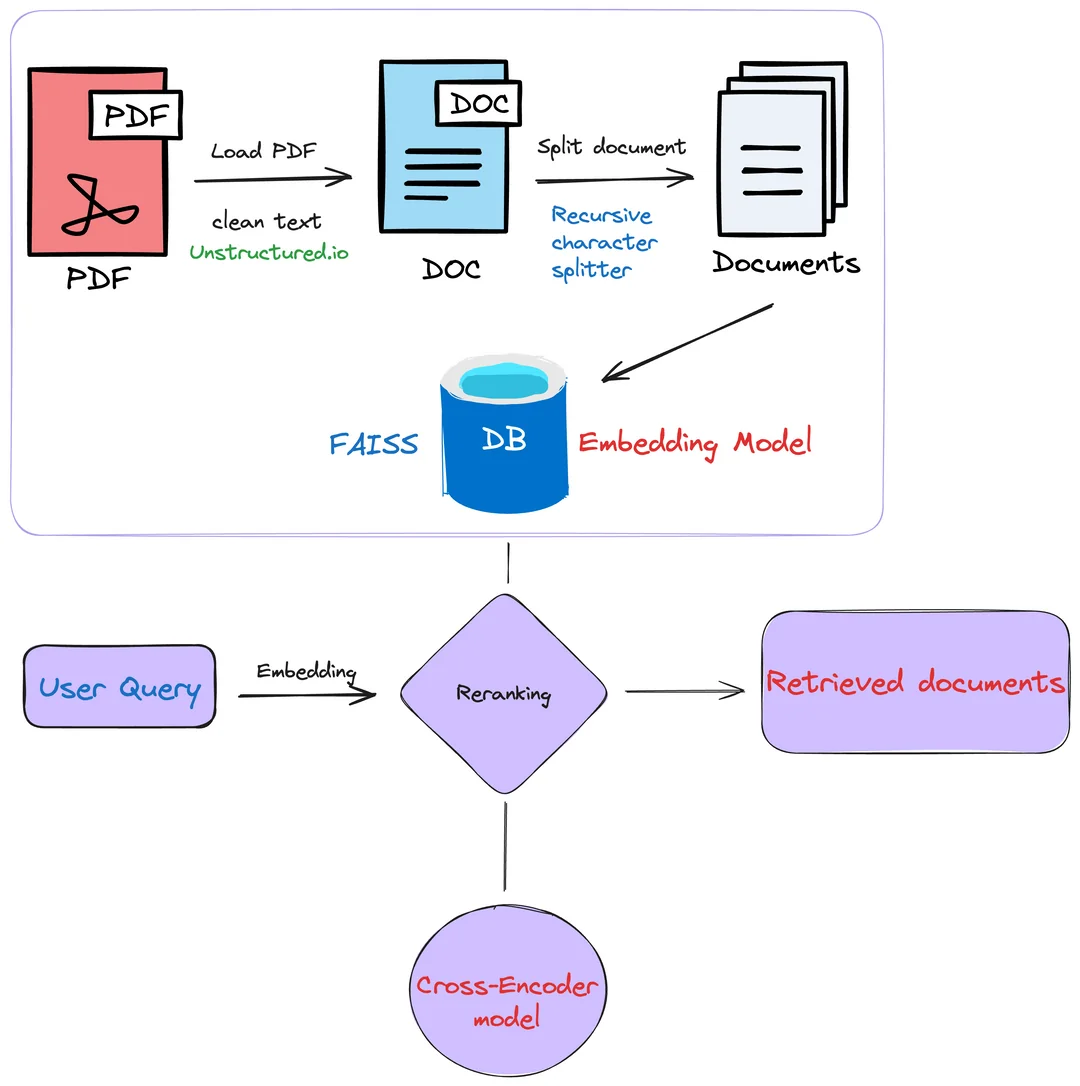
پردازش اسناد PDF برای برنامههای RAG #
این Notebook نشان میدهد چگونه میتوان از GPT-4V برای تبدیل اسناد PDF مانند اسلایدها یا خروجیهای صفحات وب به محتوای قابل استفاده برای برنامههای RAG استفاده کرد.
این تکنیک میتواند در صورتی که دادههای غیرساختارمند زیادی دارید که حاوی اطلاعات ارزشمندی هستند و میخواهید به عنوان بخشی از پایپلاین RAG خود آنها را بازیابی کنید، مورد استفاده قرار گیرد.
به عنوان مثال، میتوانید یک Knowledge Assistant بسازید که بتواند به سوالات کاربران درباره شرکت یا محصول شما بر اساس اطلاعات موجود در اسناد PDF پاسخ دهد.
درین مثال ما از اسناد مربوط به APIهای OpenAI استفاده کردهایم که شامل تکنیکهای مختلفی هستند که میتوانند به عنوان بخشی از پروژههای LLM استفاده شوند.
آمادهسازی دادهها #
در این بخش، دادههای ورودی خود را پردازش میکنیم تا برای بازیابی آماده شوند.
این کار را به دو روش انجام خواهیم داد:
- استخراج متن با
pdfminer - تبدیل صفحات PDF به تصاویر برای تحلیل آنها با
GPT-4V
میتوانید روش اول را نادیده بگیرید اگر میخواهید فقط از محتوای استنباط شده از تحلیل تصویر استفاده کنید.
تنظیمات #
باید چند کتابخانه نصب کنیم تا PDF را به تصاویر تبدیل کرده و متن را استخراج کنیم (اختیاری).
توجه: باید poppler را روی سیستم خود نصب کنید تا کتابخانه pdf2image کار کند. میتوانید دستورالعملهای نصب آن را اینجا دنبال کنید.
1%pip install pdf2image
2%pip install pdfminer
3%pip install openai
4%pip install scikit-learn
5%pip install rich
6%pip install tqdm
7%pip install concurrent
1# Imports
2from pdf2image import convert_from_path
3from pdf2image.exceptions import (
4 PDFInfoNotInstalledError,
5 PDFPageCountError,
6 PDFSyntaxError
7)
8from pdfminer.high_level import extract_text
9import base64
10from io import BytesIO
11import os
12import concurrent
13from tqdm import tqdm
14from openai import OpenAI
15import re
16import pandas as pd
17from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
18import json
19import numpy as np
20from rich import print
21from ast import literal_eval
پردازش فایل #
1def convert_doc_to_images(path):
2 images = convert_from_path(path)
3 return images
4
5def extract_text_from_doc(path):
6 text = extract_text(path)
7 page_text = []
8 return text
تست با یک مثال #
میتوانید مسیر فایل زیر را به یک فایل PDF که بر روی کامپیوترتان قرار دارد تغییر دهید.
1text = extract_text_from_doc(file_path)
تحلیل تصویر با GPT-4V
#
پس از تبدیل یک فایل PDF به چندین تصویر، از GPT-4V برای تحلیل محتوا بر اساس تصاویر استفاده خواهیم کرد.
برای اجرای کدهای زیر ابتدا باید یک کلید API را از طریق پنل کاربری گیلاس تولید کنید. برای این کار ابتدا یک حساب کاربری جدید بسازید یا اگر صاحب حساب کاربری هستید وارد پنل کاربری خود شوید. سپس، به صفحه کلید API بروید و با کلیک روی دکمه “ساخت کلید API” یک کلید جدید برای دسترسی به Gilas API بسازید.
1# imports
2from openai import OpenAI # for calling the OpenAI API
3import os
4
5client = OpenAI(
6 api_key=os.environ.get(("GILAS_API_KEY", "<کلید API خود را اینجا بسازید https://dashboard.gilas.io/apiKey>")),
7 base_url="https://api.gilas.io/v1/" # Gilas APIs
8)
9
10
11# Converting images to base64 encoded images in a data URI format to use with the ChatCompletions API
12def get_img_uri(img):
13 buffer = BytesIO()
14 img.save(buffer, format="jpeg")
15 base64_image = base64.b64encode(buffer.getvalue()).decode("utf-8")
16 data_uri = f"data:image/jpeg;base64,{base64_image}"
17 return data_uri
1system_prompt = '''
2You will be provided with an image of a pdf page or a slide. Your goal is to talk about the content that you see, in technical terms, as if you were delivering a presentation.
3
4If there are diagrams, describe the diagrams and explain their meaning.
5For example: if there is a diagram describing a process flow, say something like "the process flow starts with X then we have Y and Z..."
6
7If there are tables, describe logically the content in the tables
8For example: if there is a table listing items and prices, say something like "the prices are the following: A for X, B for Y..."
9
10DO NOT include terms referring to the content format
11DO NOT mention the content type - DO focus on the content itself
12For example: if there is a diagram/chart and text on the image, talk about both without mentioning that one is a chart and the other is text.
13Simply describe what you see in the diagram and what you understand from the text.
14
15You should keep it concise, but keep in mind your audience cannot see the image so be exhaustive in describing the content.
16
17Exclude elements that are not relevant to the content:
18DO NOT mention page numbers or the position of the elements on the image.
19
20------
21
22If there is an identifiable title, identify the title to give the output in the following format:
23
24{TITLE}
25
26{Content description}
27
28If there is no clear title, simply return the content description.
29
30'''
31
32def analyze_image(img_url):
33 response = client.chat.completions.create(
34 model="gpt-4-vision-preview",
35 temperature=0,
36 messages=[
37 {
38 "role": "system",
39 "content": system_prompt
40 },
41 {
42 "role": "user",
43 "content": [
44 {
45 "type": "image_url",
46 "image_url": img_url,
47 },
48 ],
49 }
50 ],
51 max_tokens=300,
52 top_p=0.1
53 )
54
55 return response.choices[0].message.content
تست با یک مثال #
حال میخواهیم محتوای متنی یکی از صفحات را نشان دهیم.
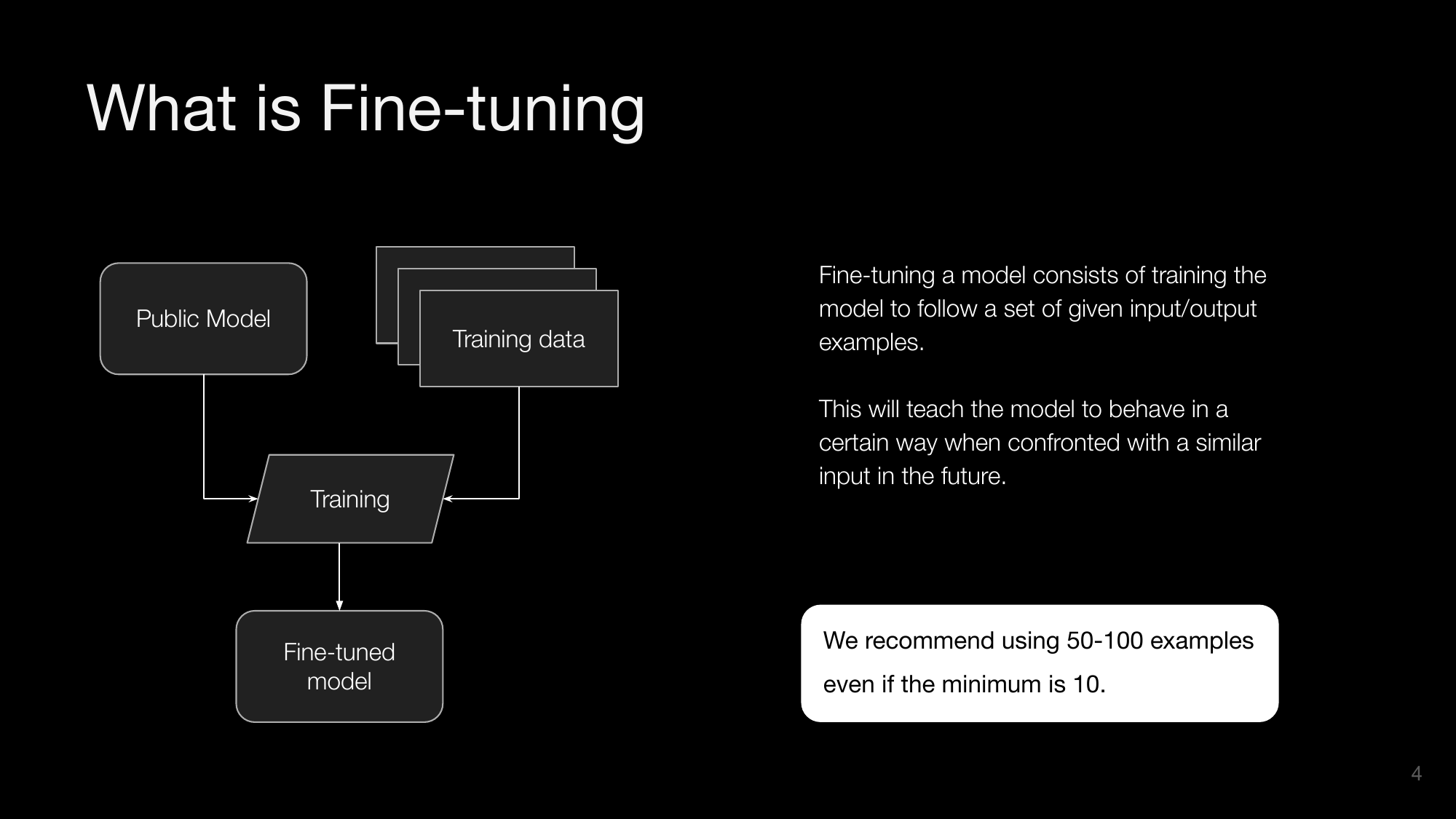
What is Fine-tuning
Fine-tuning a model consists of training the model to follow a set of given input/output examples. This will teach the model to behave in a certain way when confronted with a similar input in the future.
We recommend using 50-100 examples even if the minimum is 10.
The process involves starting with a public model, using training data to train the model, and resulting in a fine-tuned model.
پردازش همه اسناد #
حال که از درست بودن کد خود مطمین شدیم تمام فایل های موجود در پوشه را برای پردازش شدن استفاده میکنیم.
1files_path = "data/example_pdfs"
2
3all_items = os.listdir(files_path)
4files = [item for item in all_items if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(files_path, item))]
5
6def analyze_doc_image(img):
7 img_uri = get_img_uri(img)
8 data = analyze_image(img_uri)
9 return data
ما همه فایلها را در پوشه نمونه فهرست کرده و آنها را پردازش خواهیم کرد:
- استخراج متن
- تبدیل اسناد به تصاویر
- تحلیل صفحات با
GPT-4V
توجه: این کار حدود ~2 دقیقه طول میکشد. میتوانید این مرحله را نادیده بگیرید و مستقیماً فایل نتیجه را بارگذاری کنید (به زیر مراجعه کنید).
1docs = []
2
3for f in files:
4
5 path = f"{files_path}/{f}"
6 doc = {
7 "filename": f
8 }
9 text = extract_text_from_doc(path)
10 doc['text'] = text
11 imgs = convert_doc_to_images(path)
12 pages_description = []
13
14 print(f"Analyzing pages for doc {f}")
15
16 # Concurrent execution
17 with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=8) as executor:
18
19 # Removing 1st slide as it's usually just an intro
20 futures = [
21 executor.submit(analyze_doc_image, img)
22 for img in imgs[1:]
23 ]
24
25 with tqdm(total=len(imgs)-1) as pbar:
26 for _ in concurrent.futures.as_completed(futures):
27 pbar.update(1)
28
29 for f in futures:
30 res = f.result()
31 pages_description.append(res)
32
33 doc['pages_description'] = pages_description
34 docs.append(doc)
Analyzing pages for doc rag-deck.pdf
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 19/19 [00:32<00:00, 1.72s/it]
Analyzing pages for doc models-page.pdf
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 9/9 [00:25<00:00, 2.80s/it]
Analyzing pages for doc evals-decks.pdf
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 12/12 [00:29<00:00, 2.44s/it]
Analyzing pages for doc fine-tuning-deck.pdf
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 6/6 [00:19<00:00, 3.32s/it]
1# Saving result to file for later
2json_path = "data/parsed_pdf_docs.json"
3
4with open(json_path, 'w') as f:
5 json.dump(docs, f)
1# Optional: load content from the saved file
2with open(json_path, 'r') as f:
3 docs = json.load(f)
امبدینگ محتوا #
قبل از embedding محتوا، محتوای صفحات را از هم جدا میکنیم و برای هر صفحه یک بردار امبدینگ جداگانه میسازیم.
برای سناریوهای واقعی، میتوانید روشهای پیشرفتهتری برای تقسیم محتوا بررسی کنید.
1# Chunking content by page and merging together slides text & description if applicable
2content = []
3for doc in docs:
4 # Removing first slide as well
5 text = doc['text'].split('\f')[1:]
6 description = doc['pages_description']
7 description_indexes = []
8 for i in range(len(text)):
9 slide_content = text[i] + '\n'
10 # Trying to find matching slide description
11 slide_title = text[i].split('\n')[0]
12 for j in range(len(description)):
13 description_title = description[j].split('\n')[0]
14 if slide_title.lower() == description_title.lower():
15 slide_content += description[j].replace(description_title, '')
16 # Keeping track of the descriptions added
17 description_indexes.append(j)
18 # Adding the slide content + matching slide description to the content pieces
19 content.append(slide_content)
20 # Adding the slides descriptions that weren't used
21 for j in range(len(description)):
22 if j not in description_indexes:
23 content.append(description[j])
1# Cleaning up content
2# Removing trailing spaces, additional line breaks, page numbers and references to the content being a slide
3clean_content = []
4for c in content:
5 text = c.replace(' \n', '').replace('\n\n', '\n').replace('\n\n\n', '\n').strip()
6 text = re.sub(r"(?<=\n)\d{1,2}", "", text)
7 text = re.sub(r"\b(?:the|this)\s*slide\s*\w+\b", "", text, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
8 clean_content.append(text)
1# Creating the embeddings
2# We'll save to a csv file here for testing purposes but this is where you should load content in your vectorDB.
3df = pd.DataFrame(clean_content, columns=['content'])
4print(df.shape)
5df.head()
(64, 1)
| content | |
|---|---|
| 0 | Overview\nRetrieval-Augmented Generationenhanc... |
| 1 | What is RAG\nRetrieve information to Augment t... |
| 2 | When to use RAG\nGood for ✅\nNot good for ❌\... |
| 3 | Technical patterns\nData preparation\nInput pr... |
| 4 | Technical patterns\nData preparation\nchunk do... |
شروع ساخت بردار امبدینگ:
1embeddings_model = "text-embedding-3-large"
2
3def get_embeddings(text):
4 embeddings = client.embeddings.create(
5 model="text-embedding-3-small",
6 input=text,
7 encoding_format="float"
8 )
9 return embeddings.data[0].embedding
| content | embeddings | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Overview\nRetrieval-Augmented Generationenhanc... | [-0.014744381, 0.03017278, 0.06353764, 0.02110... |
| 1 | What is RAG\nRetrieve information to Augment t... | [-0.024337867, 0.022921458, -0.00971687, 0.010... |
| 2 | When to use RAG\nGood for ✅\nNot good for ❌\... | [-0.011084231, 0.021158217, -0.00430421, 0.017... |
| 3 | Technical patterns\nData preparation\nInput pr... | [-0.0058343858, 0.0408407, 0.054318383, 0.0190... |
| 4 | Technical patterns\nData preparation\nchunk do... | [-0.010359385, 0.03736894, 0.052995477, 0.0180... |
1# Saving locally for later
2data_path = "data/parsed_pdf_docs_with_embeddings.csv"
3df.to_csv(data_path, index=False)
1# Optional: load data from saved file
2df = pd.read_csv(data_path)
3df["embeddings"] = df.embeddings.apply(literal_eval).apply(np.array)
تولید با استفاده از بازیابی #
آخرین مرحله از فرآیند، تولید خروجیها در پاسخ به پرسشهای ورودی است، پس از بازیابی محتوا به عنوان زمینه برای پاسخ.
1system_prompt = '''
2 You will be provided with an input prompt and content as context that can be used to reply to the prompt.
3
4 You will do 2 things:
5
6 1. First, you will internally assess whether the content provided is relevant to reply to the input prompt.
7
8 2a. If that is the case, answer directly using this content. If the content is relevant, use elements found in the content to craft a reply to the input prompt.
9
10 2b. If the content is not relevant, use your own knowledge to reply or say that you don't know how to respond if your knowledge is not sufficient to answer.
11
12 Stay concise with your answer, replying specifically to the input prompt without mentioning additional information provided in the context content.
13'''
14
15model="gpt-4-turbo-preview"
16
17def search_content(df, input_text, top_k):
18 embedded_value = get_embeddings(input_text)
19 df["similarity"] = df.embeddings.apply(lambda x: cosine_similarity(np.array(x).reshape(1,-1), np.array(embedded_value).reshape(1, -1)))
20 res = df.sort_values('similarity', ascending=False).head(top_k)
21 return res
22
23def get_similarity(row):
24 similarity_score = row['similarity']
25 if isinstance(similarity_score, np.ndarray):
26 similarity_score = similarity_score[0][0]
27 return similarity_score
28
29def generate_output(input_prompt, similar_content, threshold = 0.5):
30
31 content = similar_content.iloc[0]['content']
32
33 # Adding more matching content if the similarity is above threshold
34 if len(similar_content) > 1:
35 for i, row in similar_content.iterrows():
36 similarity_score = get_similarity(row)
37 if similarity_score > threshold:
38 content += f"\n\n{row['content']}"
39
40 prompt = f"INPUT PROMPT:\n{input_prompt}\n-------\nCONTENT:\n{content}"
41
42 completion = client.chat.completions.create(
43 model=model,
44 temperature=0.5,
45 messages=[
46 {
47 "role": "system",
48 "content": system_prompt
49 },
50 {
51 "role": "user",
52 "content": prompt
53 }
54 ]
55 )
56
57 return completion.choices[0].message.content
1# Example user queries related to the content
2example_inputs = [
3 'What are the main models you offer?',
4 'Do you have a speech recognition model?',
5 'Which embedding model should I use for non-English use cases?',
6 'Can I introduce new knowledge in my LLM app using RAG?',
7 'How many examples do I need to fine-tune a model?',
8 'Which metric can I use to evaluate a summarization task?',
9 'Give me a detailed example for an evaluation process where we are looking for a clear answer to compare to a ground truth.',
10]
1# Running the RAG pipeline on each example
2for ex in example_inputs:
3 print(f"[deep_pink4][bold]QUERY:[/bold] {ex}[/deep_pink4]\n\n")
4 matching_content = search_content(df, ex, 3)
5 print(f"[grey37][b]Matching content:[/b][/grey37]\n")
6 for i, match in matching_content.iterrows():
7 print(f"[grey37][i]Similarity: {get_similarity(match):.2f}[/i][/grey37]")
8 print(f"[grey37]{match['content'][:100]}{'...' if len(match['content']) > 100 else ''}[/[grey37]]\n\n")
9 reply = generate_output(ex, matching_content)
10 print(f"[turquoise4][b]REPLY:[/b][/turquoise4]\n\n[spring_green4]{reply}[/spring_green4]\n\n--------------\n\n")
در زیر لیست کامل و طولانی سوال و جواب ها را مشاهده میکنید. هر سوال با استفاده از اطلاعات بازیابی شده از فایل های PDF توسط مدل پاسخ داده شده اند.
QUERY: What are the main models you offer?
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.43
Models - OpenAI API
The content lists various API endpoints and their corresponding latest models:
Similarity: 0.39
26/02/2024, 17:58
Models - OpenAI API
The Moderation models are designed to check whether content co...
Similarity: 0.39
The content describes various models provided by OpenAI, focusing on moderation models and GPT base ...
REPLY:
The main models we offer include:
- For completions: gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct, babbage-002, and davinci-002.
- For embeddings: text-embedding-3-small, text-embedding-3-large, and text-embedding-ada-002.
- For fine-tuning jobs: gpt-3.5-turbo, babbage-002, and davinci-002.
- For moderations: text-moderation-stable and text-moderation.
Additionally, we have the latest models like gpt-3.5-turbo-16k and fine-tuned versions of gpt-3.5-turbo.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
QUERY: Do you have a speech recognition model?
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.53
The content describes various models related to text-to-speech, speech recognition, embeddings, and ...
Similarity: 0.50
26/02/2024, 17:58
Models - OpenAI API
MODEL
DE S CRIPTION
tts-1
New Text-to-speech 1
The latest tex...
Similarity: 0.44
Technical patterns
Data preparation: augmenting content
What does “Augmenting content” mean?
Augmenti...
REPLY:
Yes, the Whisper model is a general-purpose speech recognition model mentioned in the content, capable of multilingual speech recognition, speech translation, and language identification. The v2-large model, referred to as "whisper-1", is available through an API and is optimized for faster performance.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
QUERY: Which embedding model should I use for non-English use cases?
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.57
The content describes various models related to text-to-speech, speech recognition, embeddings, and ...
Similarity: 0.46
26/02/2024, 17:58
Models - OpenAI API
Multilingual capabilities
GPT-4 outperforms both previous larg...
REPLY:
For non-English use cases, you should use the "V3 large" embedding model, as it is described as the most capable for both English and non-English tasks, with an output dimension of 3,072.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
QUERY: Can I introduce new knowledge in my LLM app using RAG?
Matching content:
Similarity: 0.50
What is RAG
Retrieve information to Augment the model’s knowledge and Generate the output
“What is y...
Similarity: 0.49
When to use RAG
Good for ✅
Not good for ❌
●
●
Introducing new information to the model
●
Teaching ...
REPLY:
Yes, you can introduce new knowledge in your LLM app using RAG by retrieving information from a knowledge base or external sources to augment the model's knowledge and generate outputs relevant to the queries posed.
جمعبندی #
در این Notebook، یاد گرفتیم چگونه یک پایپلاین RAG ساده بر اساس اسناد PDF توسعه دهیم. این شامل موارد زیر است:
- چگونه اسناد PDF را پردازش کنیم، با استفاده از اسلایدها و خروجی از یک صفحه HTML به عنوان مثال، با استفاده از یک کتابخانه پایتون و همچنین
GPT-4Vبرای تفسیر تصاویر - چگونه محتوای استخراج شده را پردازش کنیم، تمیز کنیم و به چندین قطعه تقسیم کنیم
- چگونه محتوای پردازش شده را با استفاده از
Gilas APIامبد کنیم - چگونه محتوای مرتبط با یک پرسش ورودی را بازیابی کنیم
- چگونه با استفاده از
GPT-4-turboپاسخی با استفاده از محتوای بازیابی شده به عنوان زمینه تولید کنیم
میتوانید تکنیکهای پوشش داده شده در این Notebook را به موارد استفاده مختلف اعمال کنید، مانند دستیارانی که میتوانند به دادههای اختصاصی شما دسترسی داشتهباشند، رباتهای خدمات مشتری یا FAQ که میتوانند از سیاستهای داخلی شما بخوانند، یا هر چیزی که نیاز به استفاده از اسناد غنی دارد که به عنوان تصاویر بهتر درک میشوند.